coal fired boiler power plant
It is undeniable, in this modern era, the need for electricity seems to be a primary need for the running of the economy, industry and our daily lives. One type of power plant that quite dominates the supply of electricity needs in the world or in Indonesia is a steam power plant.
The use of steam power has been known for a long time and even became the forerunner of the start of the industrial revolution. The workings of this system are basically fuel in the form of coal, gas ,and others are burned to produce heat energy, then the heat energy is used to heat the water that occurs in the boiler, the hot water then changes phase into pressurized steam. height and the steam is used to turn the turbine. Sounds simple, but in fact a lot of components contained in this system. Due to its complexity, in this article we will only focus on discussing the components of a boiler with coal fuel.

Boilers for power plants are generally box-shaped with a height that extends upwards, then turns at the top and returns down facing downwards, resembling the letter “n”. The basic structure in general is the bottom to accommodate combustion, then the top and the bend are filled with pipes filled with water and steam to “take” heat from the combustion, and in the last downflow area the flue gas is reused for heat. air that will re-enter and then go to the filtering process using either a scrubber or an electrostatic dust trap.

Radiation Zone
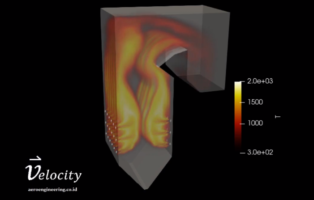
At first, this combustion was driven using diesel fuel. When the combustion is sufficient, then coal is supplied into the combustion chamber (bottom of the boiler). The fuel inlet is usually adjacent to or surrounded by the air inlet as a source of combustion oxygen. Before entering the combustion chamber, the coal supplied by the transport ship is first put into a pulverizer or coal crusher to become small chunks so that the combustion process can occur more effectively and efficiently. In this combustion zone, the walls of this room consist of pipes containing water and steam, this wall is also called a waterwall. Because the temperature is quite high, and the fire is in the middle of the combustion chamber, the most dominant heat transfer process that occurs in this zone is radiation, so this area is often categorized as a radiation zone.
There are also various combustion patterns that are applied in this combustion chamber, for example, tangential firing which shoots fire from the corners of the room and forms a fireball, there is also a type of fuel spray that faces each other, there is even a combustion type by mixing coal using sand or coal. known as fluidized bed and there are many other variations, considering that this technology is quite mature and has been used for quite a long time.
Convection Zone
After combustion occurs in the radiation zone, naturally (and some assisted by fans) the hot air will move upwards. At the top of the radiation zone, a large number of pipes have blocked the flow of the hot gas. In these pipes there is some water and some water vapor which changes phase due to the heating of the hot gas (In the supercritical boiler type, the change of water into steam occurs spontaneously without going through a mixture of water and steam). Because the dominant heat transfer between hot gas and pipes, as well as pipes and water or steam in the pipes is convection, this zone is often referred to as the convection zone.
Superheater
In this convection zone, the tubes that face the hot gas first are called superheaters. Because in this section the water that has been perfected into steam has a very high temperature and is ready to be used to turn the turbine. This steam is also known as dry steam, dry steam or superheated steam.
Reheater
The reheater is used to take advantage of the flue gas temperature which is still hot enough after passing through the superheater. The steam from the heating of the reheater is also used to turn the turbine on the secondary stage.
Economizer
The final tubing process from the convection zone is the economizer. In this section, the hot gas that has been taken heat by the superheater and reheater still has some heat that can still be utilized. Therefore, to increase the overall efficiency, the heat from the flue gas after the reheater is used to heat the feed water system which reduces the total heat required by the system to convert the water into steam.
Air-preheater
Not yet completely cold, the flue gas that passes through the economizer is reused to heat the air that will be fed into the boiler system for combustion. This heating serves to reduce the amount of fuel required to heat the intake air to the desired temperature after combustion which in turn increases the total efficiency.
Due to the complexity of the 3D flow pattern in the boiler, the thermo-chemical interaction, as well as the interaction with the existing tubing, making the boiler difficult to analyze comprehensively using analytical methods. One method that is growing rapidly for the design, optimization and failure analysis of boiler units is to use the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method, which is a modeling method using a computer to obtain flow parameters such as speed, pressure, temperature and so on.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!